

We totally assessed 37 patients and excluded ten patients who failed to meet the DSM-IV-TR criteria for GID. Our tertiary center is providing specialized and comprehensive psychiatric, psychological, surgical, and endocrine care for patients with GID.

These patients were collected over a 3 years period between January 2013 and January 2016. All cases were assessed were by two senior psychiatrists and one clinical psychologist to ensure that the DSM-IV-TR criteria were fulfilled and to confirm the diagnosis.
Mmpi 2 profiles manual#
The sample for the study consisted of 27 patients with GID that on clinical assessment met the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR) criteria for GID in adulthood and presented to the psychiatric outpatient department of tertiary care center with chief complaints of gender dysphoria and wanted to undergo sex reassignment surgery.
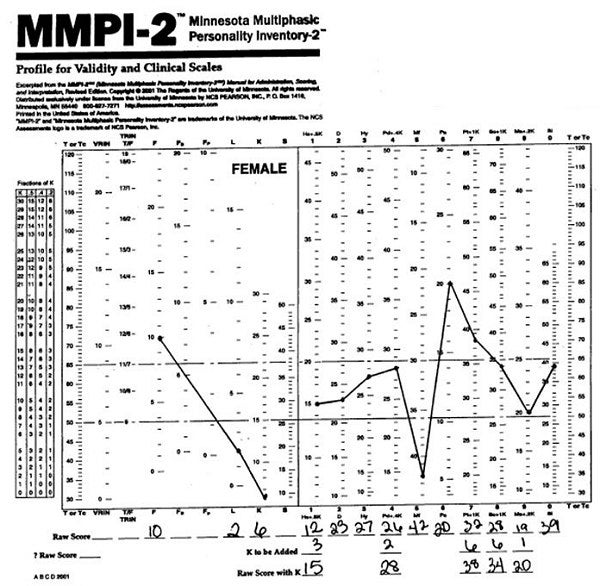
These MMPI-2 profiles were then compared based on the original gender of the patients. The aim of this study was to assess MMPI-2 profiles in patients that presented to the psychiatry department seeking a sex reassignment surgery. We undertook this study under the premise that levels of psychopathology may be minimal in patients with GID but nevertheless wanted to compare any major differences in MMPI profiles depending on the gender of origin. Indian studies on psychological assessment of patients with GID is scarce, and it is relatively uncommon as a disorder compared to other psychiatric conditions. Studies have used MMPI-2 in the general psychopathological assessment of these cases, studies have examined sex differences based on the original gender of these patients and a study has also evaluated MMPI profiles at various stages of therapy viz., during the hormonal replacement therapy phase and during the sex reassignment surgery phase and compared both profiles. MMPI-2 in the assessment of GID has been used in various phases and levels of care. Some studies with the MMPI demonstrate depression and varied psychopathology while some studies fail to demonstrate any psychopathology and may point towards GID being an isolated disorder. The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory-2 (MMPI-2) has been used in many studies to understand psychopathology in patients with GID with varying results. A variety of psychological tests, rating scales, sex role inventories, projective tests, neuropsychological assessments, and psychopathology scales have been used in the assessment of individual with GID. GID often presents to the psychiatrist when referred from the plastic surgeon whom these patients approach for sex reassignment and is often plagued with comorbid psychopathology, anxiety, lack of parental and family support and extreme psychological distress. The patient often has a discomfort with his/her biological sex and seeks help via a psychiatric consultation to get a formal approval for sex reassignment surgery to look like the opposite sex. It is suggested that the differences are a reflection of cultural and ethnic distinctions specific to each country, whereas the commonalities between the two nations indicate comparable overall profiles.Gender identity disorder (GID) is a distressing condition where there is a strong and persistent desire of wanting to belong to a sex opposite to what the patient is in and there is a persistent request towards sex reassignment surgery for the same. However, there are significant differences on specific MMPI-2 subscales including the lie, hypochondriasis, Addiction Potential Scale, overcontrolled hostility, fears, health concerns and negative treatment indicators. The overall findings indicate that MMPI-2 profile comparisons are comparable between Australian and Singaporean subjects, with considerably more similarities than differences. It was predicted that similarities across the two cultures would be observable, with differences reflected on specific scales. Participants were recruited from psychiatric outpatient clinics and consisted of 70 and 107 patients from Singapore and Australia, respectively. This study aims to extend the research on Caucasian–Chinese MMPI profiles to the countries of Singapore and Australia by examining cross-nation variations. However, there is limited research on the ability of the MMPI-2 to measure differences across diverse cultures. The use of the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory-2 (MMPI-2) as a useful measure of psychopathology has been shown in extensive studies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
